How can metal magnetic vortex pumps improve efficiency and reduce temperature rise through optimized magnetic circuit design?
Release Time : 2026-01-26
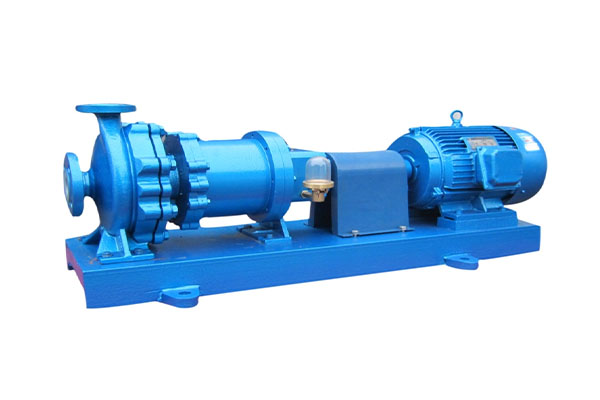
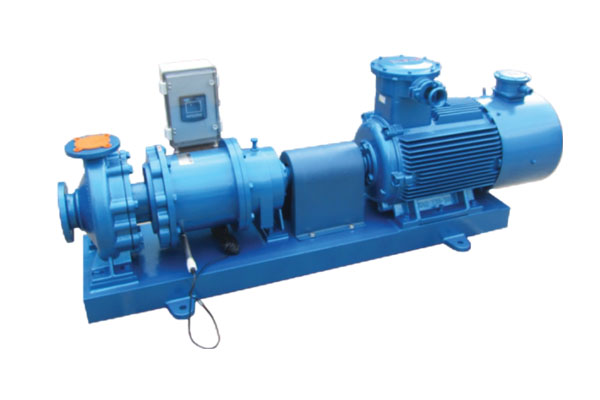
Metal magnetic vortex pumps, as leak-free and highly safe fluid transport devices, are widely used in fields with extremely high requirements for sealing and cleanliness, such as chemical, nuclear energy, and semiconductor industries. However, traditional magnetic pumps often suffer from severe overheating of the isolation sleeve due to magnetic eddy current losses, which not only reduces transmission efficiency but may also cause material demagnetization or thermal deformation, threatening operational safety. Metal magnetic vortex pumps, through systematic optimization of the magnetic circuit design, improve hydraulic efficiency by 3%–8% while significantly suppressing temperature rise, achieving efficient, reliable, and long-life operation.
1. Low Eddy Current Loss Isolation Sleeve: A Dual Breakthrough in Materials and Structure
The isolation sleeve is a key barrier for magnetic energy transmission in a magnetic pump and a major source of eddy current heating. Traditional welded isolation sleeves have weak weld areas that are prone to corrosion and perforation. However, the integral Hastelloy alloy isolation sleeve, manufactured using a stretch forming process, not only eliminates weld defects and improves pressure and corrosion resistance but also effectively suppresses induced eddy currents due to its high resistivity. Hastelloy's resistivity is approximately three times that of stainless steel. According to Joule's law, under the same alternating magnetic field, its eddy current losses are significantly reduced, thereby significantly reducing heat generation and keeping the surface temperature rise of the isolation sleeve within a safe range.
2. High-Efficiency Permanent Magnet Layout: Maximizing Magnetic Coupling and Minimizing Magnetic Leakage
The core of the magnetic circuit design lies in the arrangement of the permanent magnets. Advanced pump types employ a "Halbach array" or "multi-pole radial magnetization" structure, concentrating the magnetic field within the working air gap, enhancing the magnetic coupling torque between the inner and outer rotors, and reducing magnetic leakage to the external space. This not only improves magnetic transmission efficiency and reduces the required amount of magnets but also reduces additional eddy currents induced by stray magnetic fields in metal components, cutting heat sources at the source. Combined with precise pole pair matching and air gap control, this ensures no slippage occurs under rated torque, avoiding instantaneous overheating caused by slippage.
3. Integrated Cooling and Heat Dissipation Path: Actively Managing Heat Accumulation
Even with optimized magnetic circuits, a small amount of unavoidable eddy current heat still exists. To address this, high-end metal magnetic vortex pumps are designed with a built-in cooling circuit: some of the medium is guided through the outer wall of the isolation sleeve or the bearing cavity to carry away heat; or coolant is introduced into the pump body jacket to form forced convection cooling. Tungsten carbide sliding bearings and bushings are not only wear-resistant and resistant to particle impact, but their high thermal conductivity also allows for rapid transfer of localized frictional heat to the pump casing, preventing hotspot concentration. This "low heat generation + fast heat removal" thermal management strategy effectively maintains the magnet's operating temperature well below the Curie point, preventing demagnetization failure.
4. Hydraulic-Magnetic Synergistic Optimization: System-Level Efficiency Leap
The company's independently developed high-efficiency hydraulic model is not isolated but deeply coupled with the magnetic circuit design. CFD simulation optimizes the impeller and volute matching to reduce hydraulic losses; simultaneously, the rotor diameter and magnetic pole distribution are adjusted to ensure the optimal efficiency point coincides with the peak torque region of the magnetic drive. This mechatronic design improves overall efficiency by 3%–8% compared to traditional models, meaning lower input power and reduced heat generation at the same flow rate and head, forming a virtuous cycle of "high efficiency—low heat—high reliability".
5. Safety Redundancy Design: Eliminating Leakage Risk
It is worth noting that even with wear on the isolation sleeve, this pump model effectively prevents direct friction between the magnets and the isolation sleeve caused by rotor eccentricity through the high bending strength and wear resistance of the tungsten carbide bearings. Combined with leakage monitoring and automatic shutdown protection devices, media leakage can be avoided even under extreme operating conditions, truly achieving "intrinsic safety."
In summary, the metal magnetic vortex pump systematically solves the contradiction between efficiency and temperature rise through a high-resistivity integral isolation sleeve, efficient magnetic circuit layout, active heat dissipation mechanism, and hydraulic-magnetic synergistic optimization. It is not just a pump, but a precision engineering masterpiece integrating materials science, electromagnetics, and fluid mechanics, setting a new benchmark for the safe transportation of high-risk media.
1. Low Eddy Current Loss Isolation Sleeve: A Dual Breakthrough in Materials and Structure
The isolation sleeve is a key barrier for magnetic energy transmission in a magnetic pump and a major source of eddy current heating. Traditional welded isolation sleeves have weak weld areas that are prone to corrosion and perforation. However, the integral Hastelloy alloy isolation sleeve, manufactured using a stretch forming process, not only eliminates weld defects and improves pressure and corrosion resistance but also effectively suppresses induced eddy currents due to its high resistivity. Hastelloy's resistivity is approximately three times that of stainless steel. According to Joule's law, under the same alternating magnetic field, its eddy current losses are significantly reduced, thereby significantly reducing heat generation and keeping the surface temperature rise of the isolation sleeve within a safe range.
2. High-Efficiency Permanent Magnet Layout: Maximizing Magnetic Coupling and Minimizing Magnetic Leakage
The core of the magnetic circuit design lies in the arrangement of the permanent magnets. Advanced pump types employ a "Halbach array" or "multi-pole radial magnetization" structure, concentrating the magnetic field within the working air gap, enhancing the magnetic coupling torque between the inner and outer rotors, and reducing magnetic leakage to the external space. This not only improves magnetic transmission efficiency and reduces the required amount of magnets but also reduces additional eddy currents induced by stray magnetic fields in metal components, cutting heat sources at the source. Combined with precise pole pair matching and air gap control, this ensures no slippage occurs under rated torque, avoiding instantaneous overheating caused by slippage.
3. Integrated Cooling and Heat Dissipation Path: Actively Managing Heat Accumulation
Even with optimized magnetic circuits, a small amount of unavoidable eddy current heat still exists. To address this, high-end metal magnetic vortex pumps are designed with a built-in cooling circuit: some of the medium is guided through the outer wall of the isolation sleeve or the bearing cavity to carry away heat; or coolant is introduced into the pump body jacket to form forced convection cooling. Tungsten carbide sliding bearings and bushings are not only wear-resistant and resistant to particle impact, but their high thermal conductivity also allows for rapid transfer of localized frictional heat to the pump casing, preventing hotspot concentration. This "low heat generation + fast heat removal" thermal management strategy effectively maintains the magnet's operating temperature well below the Curie point, preventing demagnetization failure.
4. Hydraulic-Magnetic Synergistic Optimization: System-Level Efficiency Leap
The company's independently developed high-efficiency hydraulic model is not isolated but deeply coupled with the magnetic circuit design. CFD simulation optimizes the impeller and volute matching to reduce hydraulic losses; simultaneously, the rotor diameter and magnetic pole distribution are adjusted to ensure the optimal efficiency point coincides with the peak torque region of the magnetic drive. This mechatronic design improves overall efficiency by 3%–8% compared to traditional models, meaning lower input power and reduced heat generation at the same flow rate and head, forming a virtuous cycle of "high efficiency—low heat—high reliability".
5. Safety Redundancy Design: Eliminating Leakage Risk
It is worth noting that even with wear on the isolation sleeve, this pump model effectively prevents direct friction between the magnets and the isolation sleeve caused by rotor eccentricity through the high bending strength and wear resistance of the tungsten carbide bearings. Combined with leakage monitoring and automatic shutdown protection devices, media leakage can be avoided even under extreme operating conditions, truly achieving "intrinsic safety."
In summary, the metal magnetic vortex pump systematically solves the contradiction between efficiency and temperature rise through a high-resistivity integral isolation sleeve, efficient magnetic circuit layout, active heat dissipation mechanism, and hydraulic-magnetic synergistic optimization. It is not just a pump, but a precision engineering masterpiece integrating materials science, electromagnetics, and fluid mechanics, setting a new benchmark for the safe transportation of high-risk media.